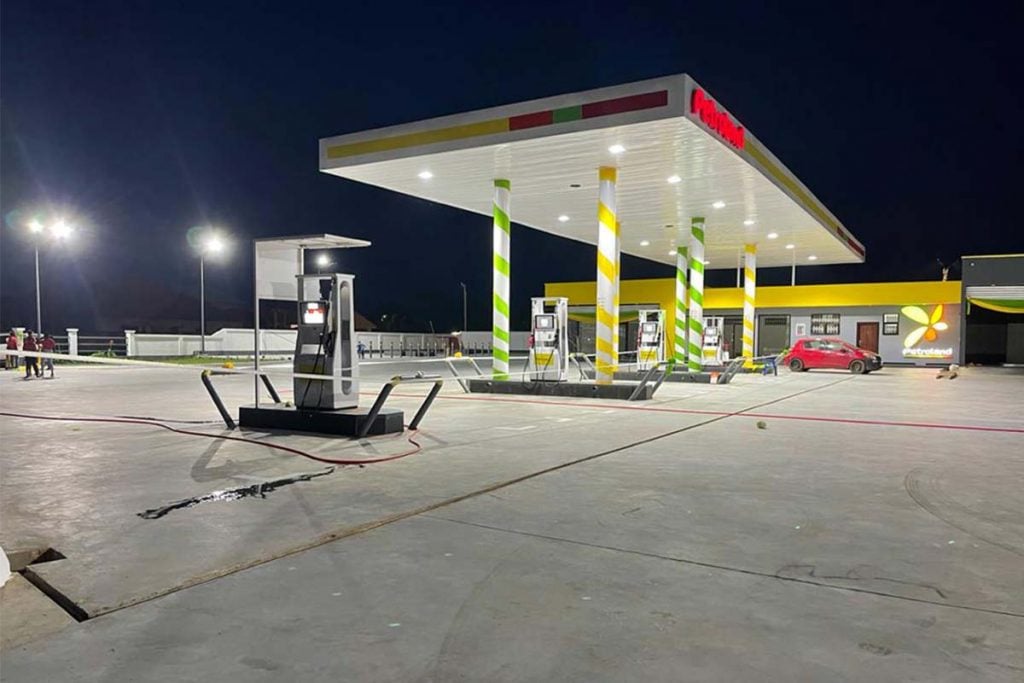
ATEX light – ZGSM gas station LED lighting
ATEX light – ZGSM gas station LED lighting
Introduction
Explosive atmospheres can be caused by flammable gases, mists or vapors, or combustible dusts. If there is enough of this substance, mixed with air, then it only needs an ignition source to cause an explosion. Explosions can cause loss of life and serious injuries as well as significant damage. Two widely used methods of reducing risk, 1. prevent the release of hazardous substances that can create an explosive environment, 2. prevent sources of ignition. When carrying out production operations in these areas, the use of explosion-proof products plays a very important role in safety.
Typically these areas include oil/gas rigs, process refineries, chemical production facilities, flammable liquid storage facilities, fuel transportation, gas stations, paint production, paper manufacturing and more. It helps us a lot when we use the right equipment in these areas. A “hazardous area” is defined as an area where the atmosphere contains or may contain sufficient quantities of flammable or explosive gases, dusts or vapors. In such an atmosphere, fire or explosion may occur when three basic conditions are met. This often referred to as the “hazardous area” or “combustion” triangle. They are air, ignition source, combustibles (flammable gas, mist or steam, combustible dust). This article mainly introduces ATEX related standards, classification of explosive atmospheres, ATEX markings, explosion protection equipment selection, and ZGSM ATEX lighting solutions etc.
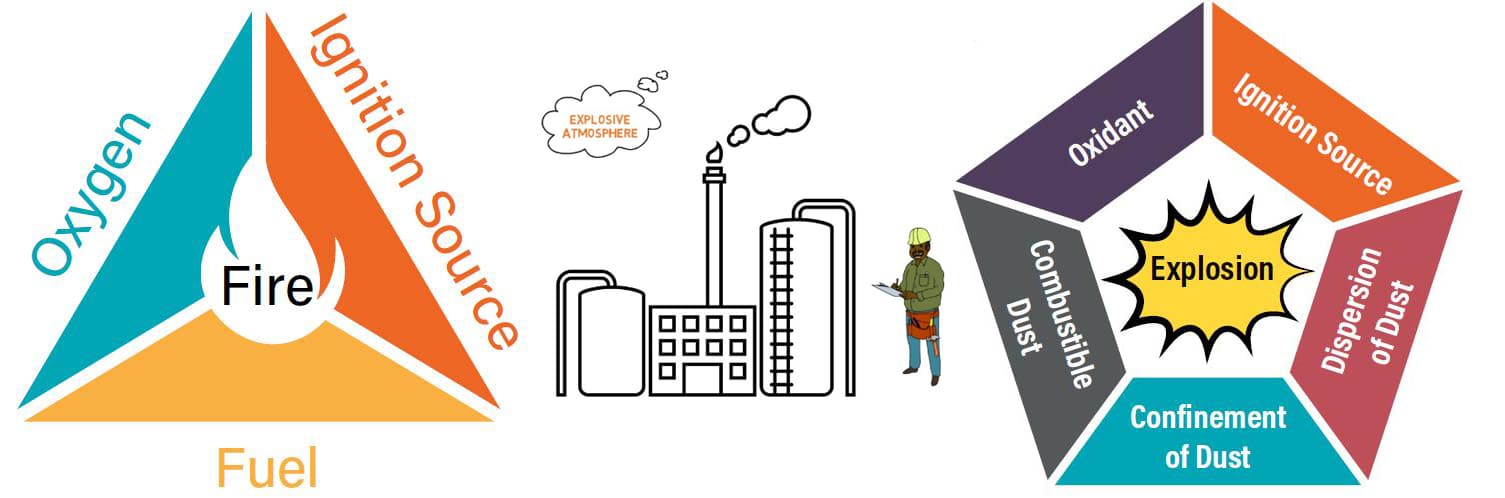
What’s ATEX?
ATEX is the abbreviation of “ATmosphères EXplosibles” in French. It is an explosion-proof directive of the EU CE compulsory certification. Manufacturers of equipment intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres apply the terms of the ATEX directive and put CE mark on their electrical equipment (for example LED light). The core requirements of the ATEX explosion-proof directive: to protect the safety and health of people, and under certain circumstances to protect the health and property safety of livestock, especially to protect workers from the hazards of equipment and systems suitable for potentially explosive environments. After obtaining ATEX, suppliers or manufacturers can sell their explosion-proof equipment anywhere in Europe without considering the application of other more requirements. For example, for the light which should be used in gas station, we must choose ATEX certificated canopy light.
In Europe, ATEX usually chooses the following two directives to control explosive atmospheres.
1) Directive 99/92/EC (also known as “ATEX 137” or “ATEX Workplace Directive”) on minimum requirements for improving the health and safety protection of workers at potential risk in explosive atmospheres. The text of the Directive and supporting guidance developed by the IEC are available on the IEC website.
2) Directive 2014/34/EU (also known as “ATEX 114” or “ATEX Equipment Directive”), an approximation of the laws of the Member States concerning equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres. The text of the Directive and supporting guidance developed by the IEC are also available on the IEC website.
The test standards corresponding to the above directives were later issued by the International Electrotechnical Commission 60079 series of standards, which define the classification system for places, as well as the classification and test systems for equipment suitable for hazardous locations (called “Ex equipment”). Below we list some of the main standards that apply.
• IEC/EN 60079-0: Products for explosive gas atmospheres – General rules
• IEC/EN 60079-1: Explosive atmospheres – Part 1: Flameproof enclosure “d” protective equipment
• IEC/EN 60079-7: Explosive atmospheres – Part 7: Equipment protection with increased safety “e”
• IEC/EN 60079-11: Explosive atmospheres – Part 11: Equipment protected by intrinsic safety “i”
• IEC 60079-10-1 includes the classification of explosive gas atmospheres, and IEC 60079-10-2 the classification of explosive dust atmospheres.
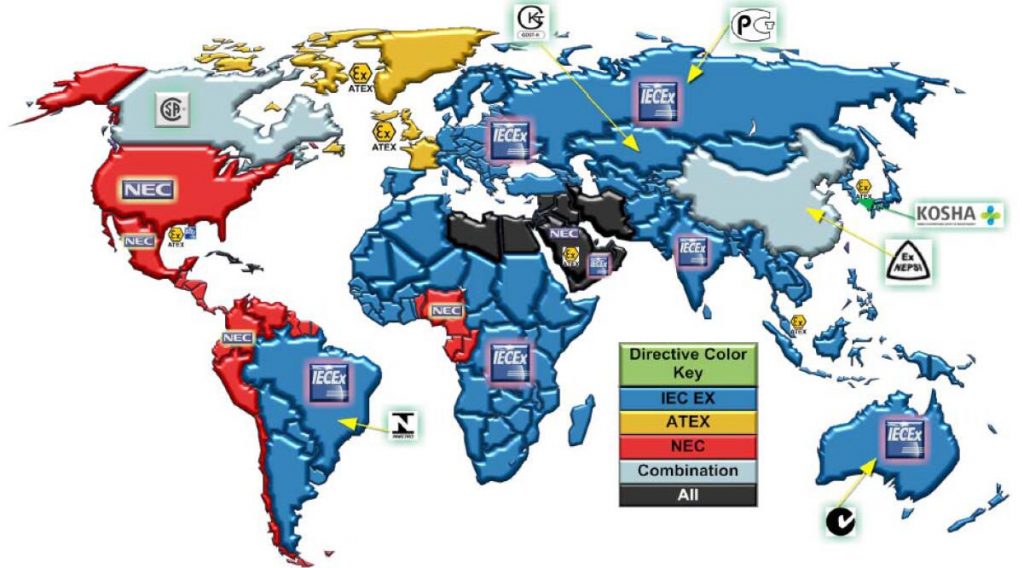
IEC or NEC
ATEX is the “Equipment and Protection System for Potentially Explosive Environments” directive adopted by the European Commission. Its purpose is to create a single market within Europe, eliminate technical barriers to trade, and ensure the free circulation of equipment intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres among its member states. The directive covers the classification of mining and non-mine equipment (including mechanical equipment and electrical equipment) and potentially explosive atmospheres. It also stipulates the basic requirements for the application of equipment intended for potentially explosive atmospheres, as well as conformity assessment procedures for equipment that must be used before entering the European market.
The North American explosion-proof certification system (hereinafter referred to as the NEC-National Electrical Code system), and it has great differences from European ATEX system. The classification and grouping of explosive substances, the division of hazardous locations, explosion-proof protection methods, installation wiring between them differs from each other in a certain degree. At present, the North American explosion-proof certification is divided into two systems, Division and Zone. The Division system adopts the explosion-proof mark of the United States, and the Zone system adopts the same explosion-proof standard as the IEC system.
Comparing NEC and IEC these two hazardous area classification systems is not easy. They are both good systems and were developed independently of each other. Each has its own method of regional classification, and each has its own advocates and approval organizations. Neither system has been proven to be more secure than the other. Currently, the IEC system is widely used in the chemical and petrochemical industries in most parts of the world (except the United States), while the latter is mainly in North America and some countries in the South.
What’s the explosive atmospheres and their classifications?
An explosive environment means that under atmospheric conditions, a mixture of flammable substances in the form of gas, vapor or dust and air can keep burning and propagating itself after being ignited. Explosive atmospheres are divided into explosive gas atmospheres and explosive dust atmospheres according to the properties of flammable substances. The former flammable substances exist in the form of gas or vapor, and the latter flammable substances exist in the form of dust.
Many workplaces may contain or have activities that create an explosive or potentially explosive atmosphere. Examples include workplaces where work activities generate or release flammable gases or vapors, such as car painting, or where fine organic dust is handled, such as grain flour or wood.
What’s the classification of hazardous areas?
Hazardous areas(explosive atmospheres) are classified according to the frequency and duration of explosive atmospheres. The classification of explosive areas for two types of substances, gas and dust, is roughly as follows.
Explosive area classifications for gases, vapors and mists are as follows:
- Zone 0: A place where an explosive atmosphere exists continuously or for a long time or frequently, and the explosive atmosphere contains a mixture of dangerous substances in the form of gas, vapor or mist.
- Zone 1: During normal operation, an explosive atmosphere containing a mixture of hazardous substances in the form of gas, vapor or mist may occasionally occur.
- Zone 2: A place where an explosive atmosphere consisting of a mixture of hazardous substances in the form of gas, vapor or mist and air is unlikely to occur during normal operation, but if it does, it will only last for a short period of time.
For dust, explosive areas are classified as follows:
- Zone 20: A place where an explosive atmosphere exists continuously, for a long time or frequently in the form of combustible dust clouds in the air.
- Zone 21: During normal operation, an explosive atmosphere, such as a cloud of combustible dust, may occasionally be present.
- Zone 22: A place where an explosive atmosphere in the form of a cloud of combustible dust is unlikely to occur under normal conditions.
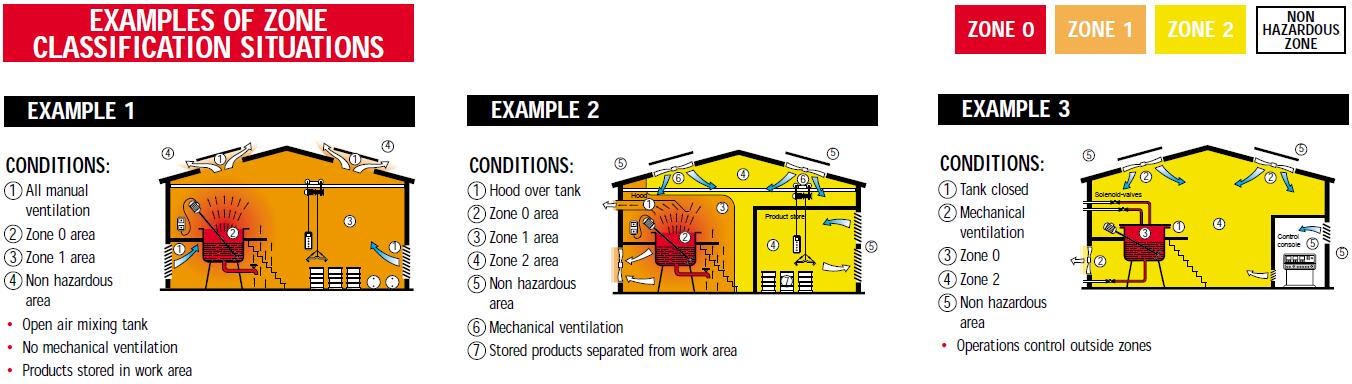
How to determine the classification of hazardous area?
In practical application, how to identify the classification of hazardous areas? We believe that it should be determined according to the production conditions, time of duration, frequency of release, and ventilation of the explosive mixture. Below we list three questions that we often need to confirm in order to check the classification of hazardous area.
1. What is emission level of gas/vapor?
a) continuous, b) first level emission (released during normal operation), c) second level emission (released during abnormal operation)
2. What type of openings currently exist?
a) continuously open, b) normally closed, c) weatherproof, d) emergency open only
What is ventilation?
a) very good, b) good, c) poor
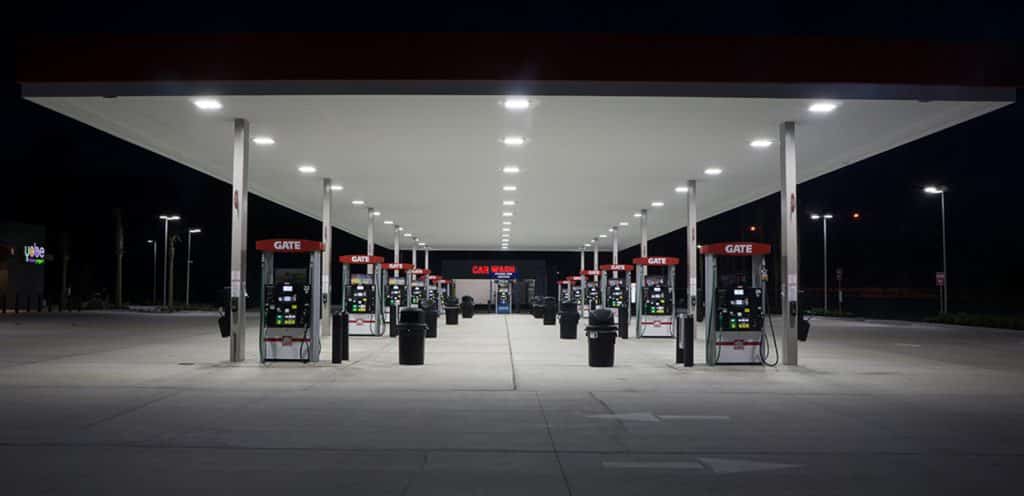
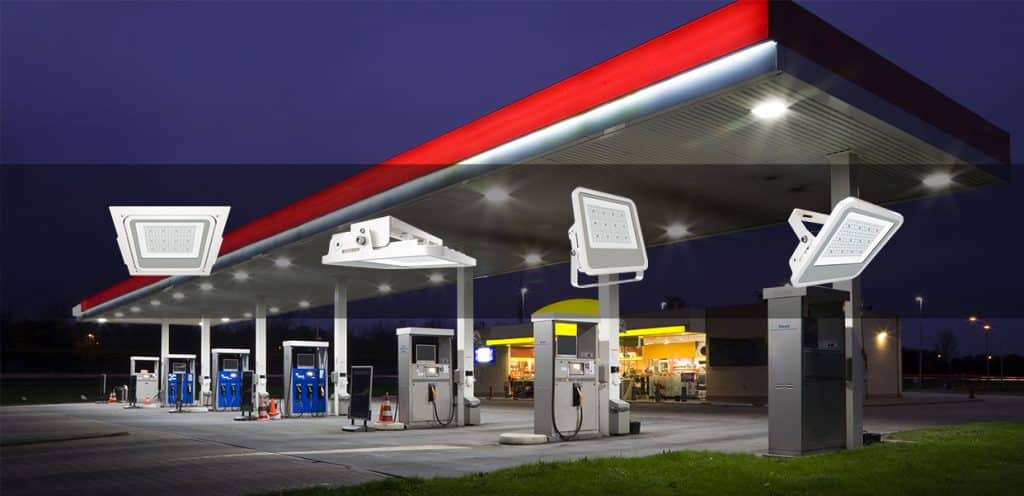
By comparing the answers of these questions, we can derive what type of hazardous zone that this area region should be classified as. Below we list three common scenarios, and what type of area that each area should be classified as. This also can be applied into gas station area classification. For example, we don’t need ATEX street light to illuminate the road/entrance of gas station, but we need ATEX canopy light to installed under gas station canopy.
How to check ATEX certificate?
How to read the ATEX marking of the product? We think we should start with Group, Categories, Types of Protection, Gas group/dust group, Temperature. The following is a typical marking of ATEX light.
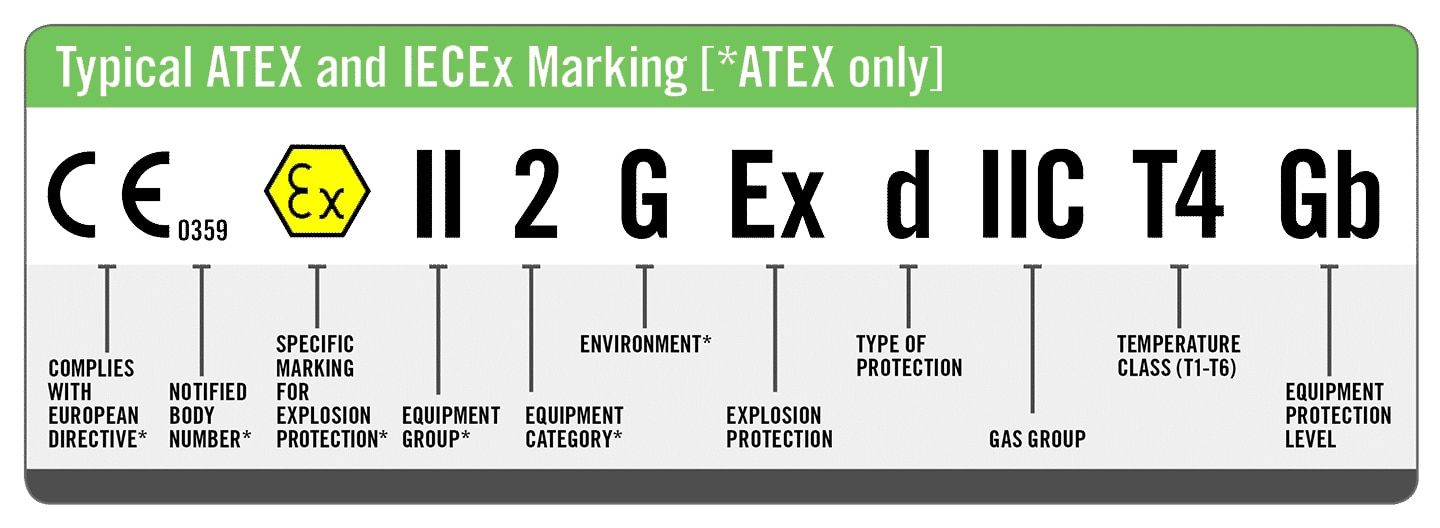
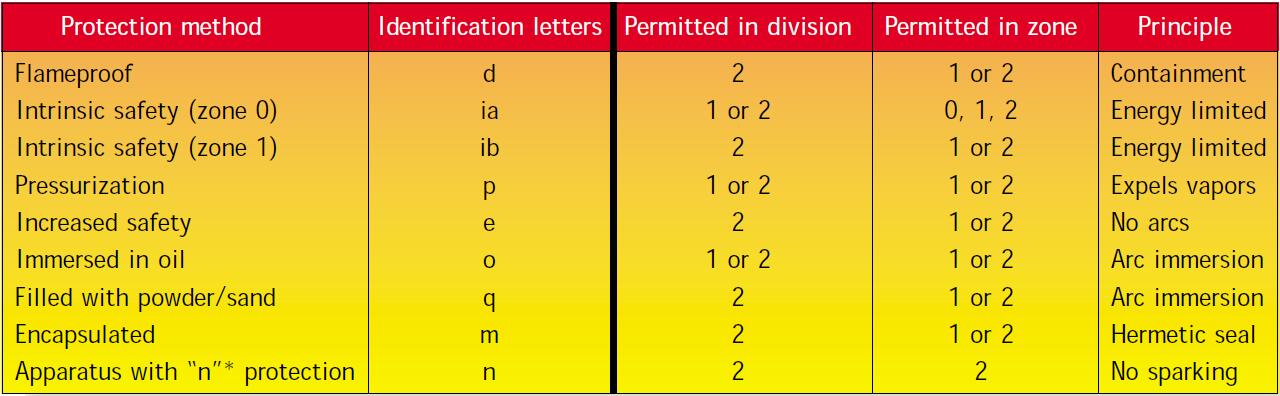
Below we give the areas where different protection types of explosion-proof products(ATEX light) are suitable.
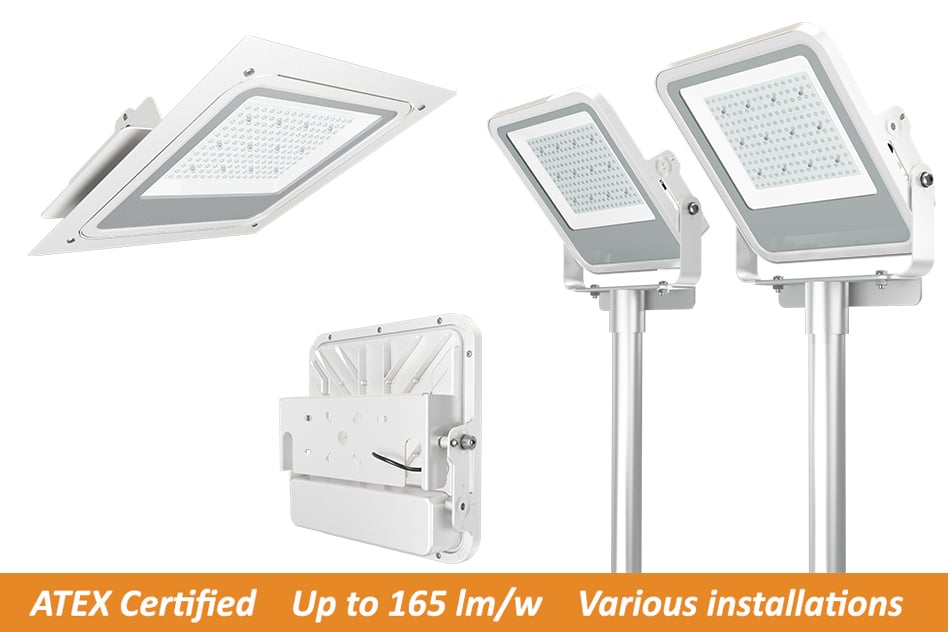
ZGSM ATEX lights
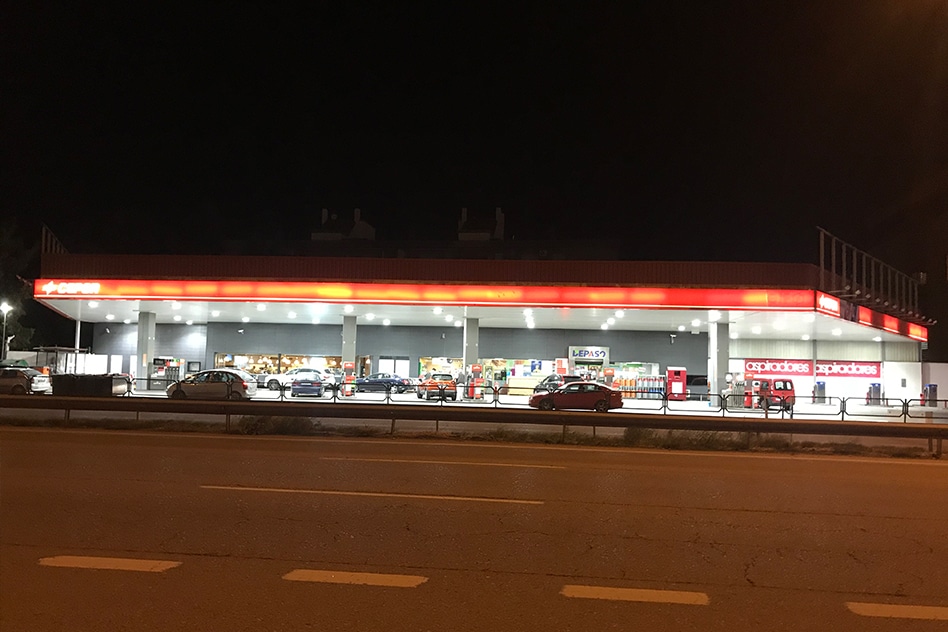
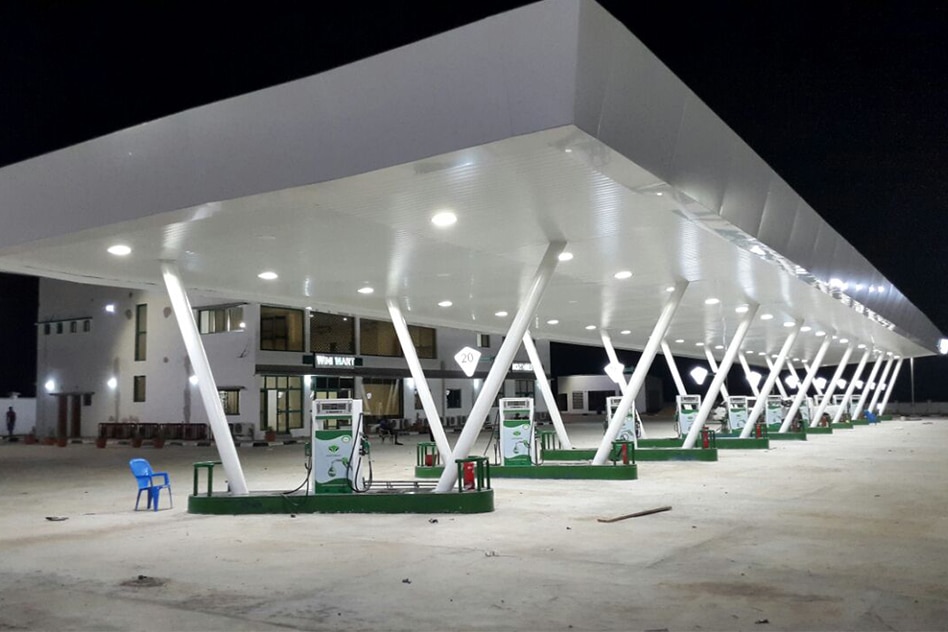
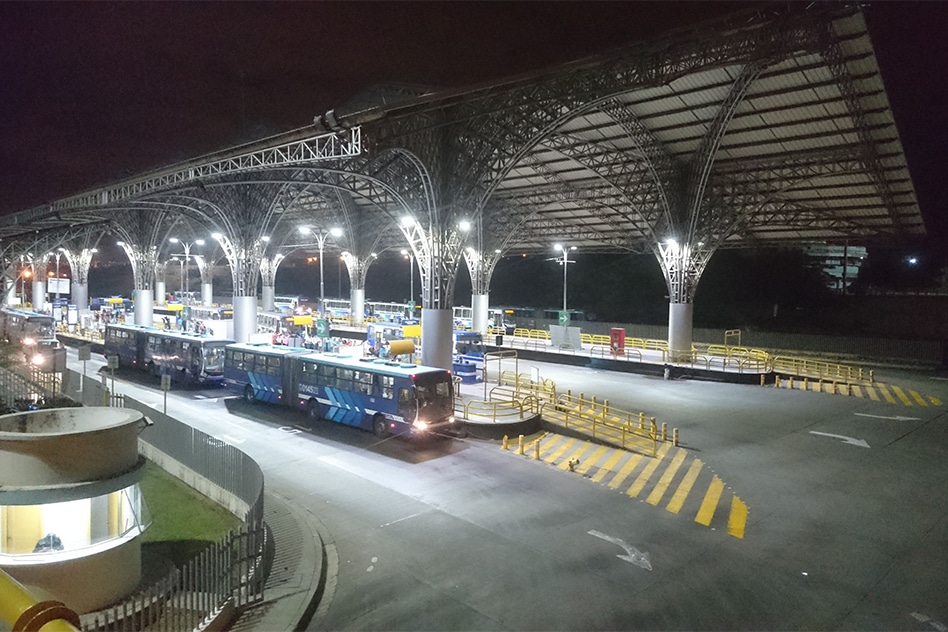
Since its establishment in 2005, ZGSM has developed lots of LED lights. The ATEX canopy lights can be used for gas station lighting. The ATEX certificated flood light can be used for work areas in explosive atmospheres. And normal street light can be used for lighting the entrance or road of service station.
Summary
This article briefly introduces the relevant knowledge of ATEX, including the concept of ATEX, what is an explosive atmosphere, how to distinguish the types of explosive atmospheres, and how to know the meaning of ATEX marking, as well as the selection of explosion-proof products, etc. We recognize manufacturers who apply the terms of the ATEX directive and affix the CE mark so that the product (equipment for potentially explosive atmospheres) can be sold anywhere in Europe without considering the application of other further requirements. At the same time, the classification of explosion-proof areas and the selection and application of explosion-proof products are also quite different in different regions, such as North America and Europe. The ultimate goal of the implementation of explosion-proof instructions is to enable users to choose explosion-proof products reasonably, so as to ensure personal health and property safety in an explosion-proof environment. These are beneficial to manufacturers, users and end consumers. It is also very necessary for our manufacturers to understand these. As a manufacturer of LED lamps (street lamps, floodlights and gas station lamps, etc.), we can clearly understand what kind of products should be recommended in what kind of places, so that customers can finally make the right choice.
Related Products
Related Blogs
Related Cases
People also ask
Author introduction

Hello Customers,
My name is Taylor Gong, I’m the product manager of ZGSM Tech. I have been in the LED lights industry for more than 13 years. Good at lighting design, street light system configuration, and bidding technology support. Feel free to contact us. I’m happy to provide you with the best service and products.
Email: [email protected] | WhatsApp: +8615068758483


































