Light distribution of outdoor luminaire and their applications
Light distribution of outdoor luminaire and their applications
Introduction
There are many important factors to consider when choosing the right LED outdoor luminaires: lumens per watt, heat dissipation, power performance, warranty, color temperature and color rendering index are all very important, as well as the light distribution. Light distribution is basically a projected pattern of street lights and floodlights throwing light onto a surface. If you know how to lay out your light fixtures based on using the right LED light and the correct light distribution, you will get better lighting effects where you can reduce the number of LED light fixtures and wattage at the same time. This is not only conducive to the planning of the project, but the project must also be very energy efficient and meet the project requirements. Therefore, the correct light distribution of LED light is very important for outdoor luminaires.
The light distributions are frequently employed in parking lot illumination, area lighting, floodlighting, roadway lighting or others. For street areas, we worry about the safety of drivers and passersby. Factors such as intensity, brightness, glare, and lighting coverage form the lighting distribution of LED lights. Several organizations have classified the lighting distribution which are aiming to select the most suitable LED street lights according to different road conditions to ensure safety. Type I, Type II, Type III, Type IV, or Type V light distribution are the five primary forms of light distribution patterns recognized in street lighting and parking lot lighting. For other outdoor lighting projects such as stadiums, squares, factory perimeters, billboards, roundabouts, etc., we also need to pay attention to these issues. The lamps involved are mainly floodlights and stadium lights. NEMA classifies the lighting distribution of these luminaires. This article will introduce the main basis for the classification of LED lighting distribution of these lamps, the different classification characteristics, and their applications.

IESNA light distribution types
This lighting classification system is mainly based on the shape of the lighting area of the luminaire. It is generally used in street and area lighting fixtures to determine what light distribution is reasonable. IESNA types are defined by the highest and 50% candela intensity which is also called luminous intensity distribution. The IESNA type classification is established by measuring where most of the light falls on the grid. This classification relates to lights crossing the road and lights along the road. The lateral light distribution depends on the position of the half-maximum candela point in the position across the road. According to this, it can be divided into TypeⅠ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ and ⅤS. However we normally called Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4 or Type 5 light distribution because it’s not very easy to enter roman numerals. See the table 1 below for half-maximum candela points of different light distributions, spectrum diagrm and corresponding applications. Vertical light distribution depends on the position of the maximum candela point in position along the road. According to this, the light distribution can be classified as Short (S), Medium (M), or Long (L).
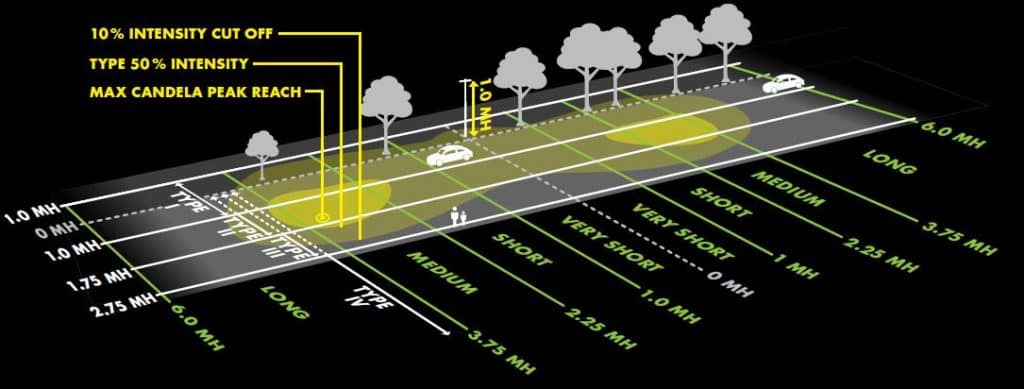
| Type | Half-maximum candela point | Light distribution pattern | Application | Photo |
| Type Ⅰ: | Falls between 1 MH on the house side and 1 MH on the street side of the luminaire position | Narrow symmetric pattern | Walkways, paths, roadway | 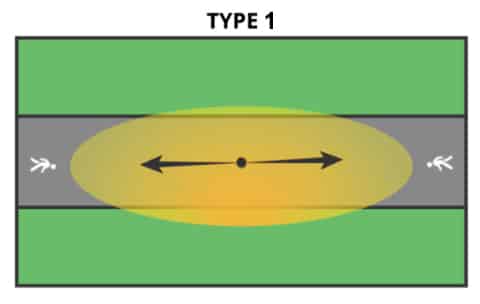 |
| Type Ⅱ | Falls between 1 MH and 1.75 MH on the street side of the luminaire position | Narrow asymmetric pattern | Walkways, roadways and bike paths | 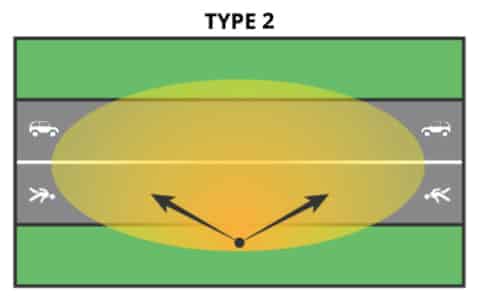 |
| Type Ⅲ | Falls between 1.75 MH and 2.75 MH on the street side of the luminaire position | Wide asymmetric pattern | Roadway, highway, parking, other area light applications | 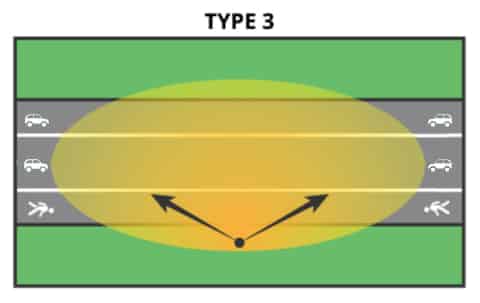 |
| Type Ⅳ | Falls beyond 2.75 MH but less than 3.7 MH on the street side of the luminaire position | Asymmetric forward throw pattern | Wall mount or pole mount perimeter applications | 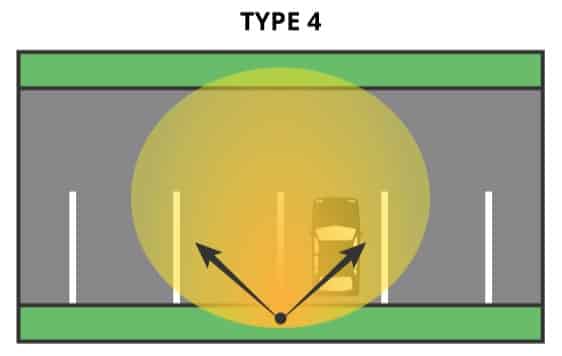 |
| Type Ⅴ | Circularly symmetrical around the luminaire position | Symmetrical circular pattern | Parking and area lighting | 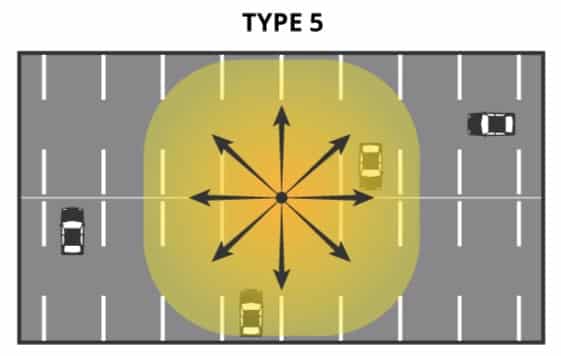 |
| Type VS | Essentially the same at all lateral angles | Symmetrical square pattern | Large areas, like the parking lot and the square | Almost same as above |
| Type | maximum candela point | Suggested Pole distance | Remarks |
| Very short | Falls between -1 MH and 1 MH along road | 1MH | Suggested Pole distance can be more than 1MH which is based on lighting design |
| Short | Falls between 1.0 and 2.25 MH along road | 1.0 to 2.25 MH | Suggested Pole distance can be more than 2.25MH which is based on lighting design |
| Medium | Falls between 2.25 and 3.75 MH along road | 2.25 to 3.75 MH | Suggested Pole distance can be more than 3.75MH which is based on lighting design |
| Long | Falls between 3.75 and 6.0 MH along road | 3.75 to 6.0 MH | Suggested Pole distance can be more than 6.0MH which is based on lighting design |
BUG rating as per IESNA
This light distribution system is based on the proportional distribution of the lumens of LED street light fixtures or flood light fixtures in three main solid angles, namely forward light, back light and uplight. These are lights in front of the luminaire, behind the luminaire, and above the luminaire. These solid angles are parts of the entire 4π solid angle around the luminaire, and these primary solid angles are further divided into 10 secondary solid angles. By calculating the lumen output in these secondary solid angles we can get BUG ratings for the ratio of lumens contained in solid angles. The BUG rating stands for backlight, uplight and glare. Backlight (B) is light directed behind the lighting fixture, uplight (U) is any light directed above the level of the lighting fixture, and glare (G) is the amount of light emitted by the lighting fixture at high angles. By this, luminaires can also be classified, evaluated and compared based on the scores of luminaires or luminaire lumens contained in each solid angle.
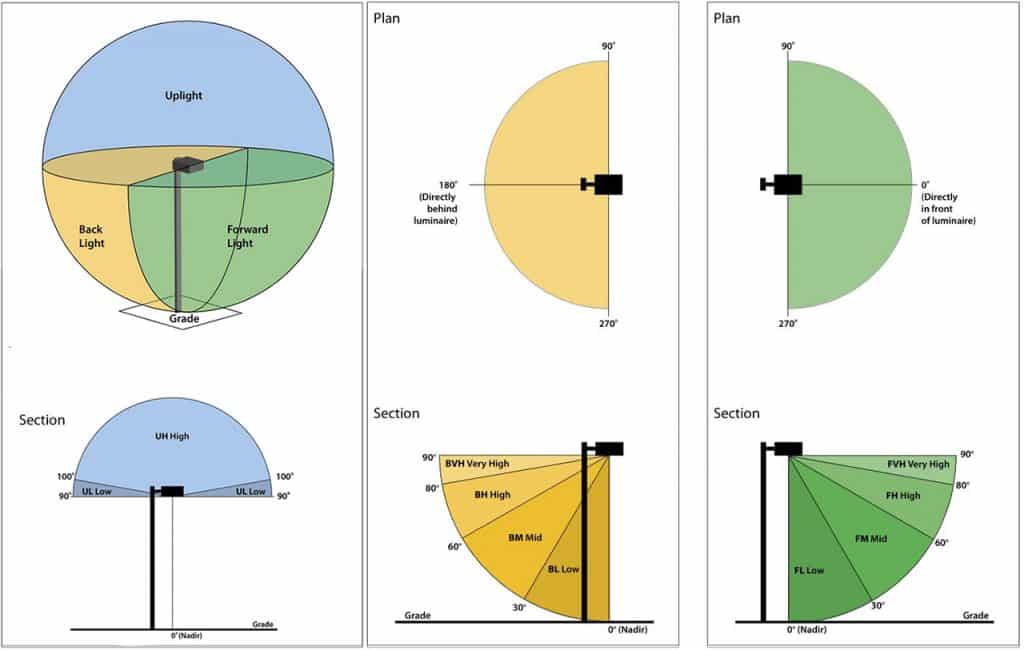
Luminaires were assessed and classified for light trespass, sky glow, and high angle brightness potential of a luminaire using the LCS described above. The lumen limit per secondary solid angle establishes a BUG rating for the luminaire. Tables 3, 4 and 5 show the individual secondary solid angles, along with the corresponding lumen limits for each of the different components. Outdoor luminaires are assigned a BUG rating by comparing the lumen output of the luminaire’s backlight, uplight, and glare areas to the maximum lumens allowed in these tables. Ratings for B, U, and G range are from 0 (most limited) to 5 (most lenient). For example, the most common, we hope that the uplight of the street light is o, which has less impact on the environment. At the same time, on highways or country roads, we hope that there will be less backlight, because in these places, the existence of backlight is basically meaningless.
| Secondary Solid Angle | B0 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 |
| BH | 110 | 500 | 1000 | 2500 | 5000 | >5000 |
| BM | 220 | 1000 | 2500 | 5000 | 8500 | >8500 |
| BL | 110 | 500 | 1000 | 2500 | 5000 | >5000 |
| Secondary Solid Angle | U0 | U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | B5 |
| UH | 0 | 10 | 100 | 500 | 1000 | >1000 |
| UM | 0 | 10 | 100 | 500 | 1000 | >1000 |
| FVH | 10 | 75 | 150 | >150 | N/A | N/A |
| BVH | 10 | 75 | 150 | >150 | N/A | N/A |
| Secondary Solid Angle | G0 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 |
| FVH | 10 | 250 | 375 | 500 | 750 | >750 |
| BVH | 10 | 250 | 375 | 500 | 750 | >750 |
| FH | 660 | 1800 | 5000 | 7500 | 12000 | >12000 |
| BH | 100 | 500 | 1000 | 2500 | 5000 | >5000 |
Cutoffas per IESNA
This light distribution classification is mentioned on IES LIGHTING HANDBOOK 9TH EDITION. However the LCS supersedes the previous IES cutoff classifications of full-cutoff, cutoff, semi-cutoff, and non-cutoff. But we can still find it in the IES files of LED light. So let’s briefly introduce something about it.
Full Cutoff – A luminaire light distribution with zero candela (intensity) at an angle of 90 degrees or above. Additionally, the candela per 1000 lamp lumens does not exceed 100 (10%) at a vertical angle of 80 degrees. This applies to all lateral angles around the luminaire.
Cutoff. A luminaire light distribution is designated as cutoff when its intensity per 1000 lamp lumens does not exceed 25 (2.5%) at an angle of 90° above nadir (horizontal), and 100 (10%) at a vertical angle of 80° above nadir. This applies to any lateral angle around the luminaire. (In some cases the cutoff distribution may meet the requirements of the semicutoff distribution.)
Semi-Cutoff – A luminaire light distribution where the candela per 1000 lumens does not exceed 50 (5%) at an angle of 90 degrees or above nardir. Additionally, the candela per 1000 lamp lumens does not exceed 200 (20%) at a vertical angle of 80 degrees. This applies to any lateral angle around the luminaire. (In some cases the semicutoff distribution may meet the requirements of the noncutoff distribution.)
Non-Cutoff – A luminaire light distribution where there is no candela restriction at any angle. This means there will be light intensity at an angle of 90 degrees or above.
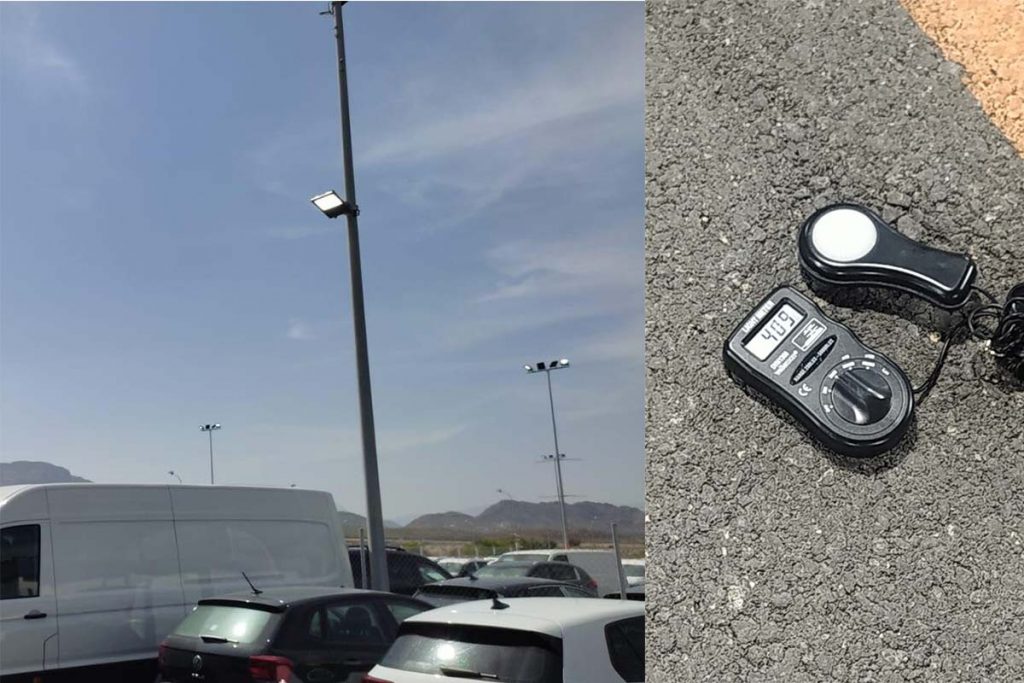
Check to see light distribution of ZGSM LED lights
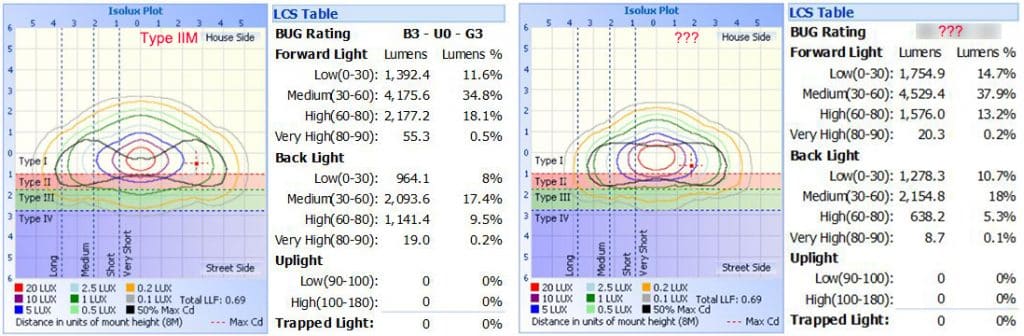
Based on above information regarding IESNA lighting classification definition, let’s try to see which IESNA type and BUG rating that below IES belongs to. Firstly for the lateral light distribution, it should be Type II because the half maximum candela points located in position Type II area. Then the vertical light distribution should be Medium light distribution. So finally it should be Type IIM. As to BUG rating, the B rating should be B3 according to table 1.1, U rating should be 0 since there are no uplights for ZGSM LED street lights, and G rating should be 3 according to table 1.3, then the final BUG rating should be B3-U0-G3. Now it’s your turn to check the right IES information which is belong to our Rifle 80W street light. Can you get your checking result that which IESNA type and BUG rating of this street lamps should be? I think you can do it, but if you can not you can check with us to get the final result.
NEMA light distribution for sports and flood lighting
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) has established a luminaire classification system based on the distribution of flux within the beam produced by the luminaire. Mainly used for stadium lighting and floodlight fixtures. From narrowest to widest beam, seven profiles are defined, with narrow beam angle, medium beam angle and wide beam angle. It’s from Type 1 to Type 7 respectively. It uses beam angle and field angle like other classifications to specify the distribution characteristics of luminaires. The beam angle is defined as the maximum angle measured from the center of the distribution, which is the angle between the two beams where the intensity drops to 0.50 of the maximum light intensity value. The field of view is defined as the maximum angle measured from the center of the distribution, which is the angle between the two beams where the intensity drops to 0.10 of the maximum light intensity value. The figure below gives an example, we can see that the general field of view angle is greater than the beam angle, which we need to distinguish.
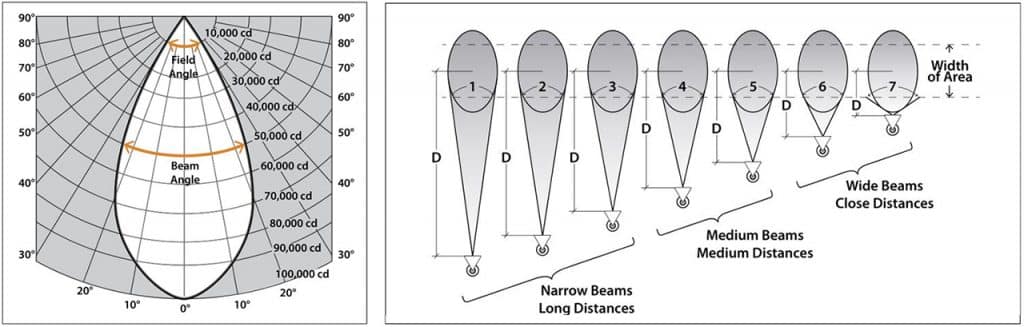
| Beam Type | Field Angle Range (degrees) | Projection Distance (D) |
| Type 1 | 10 to 18 | 240 ft and greater |
| Type 2 | > 18 to 29 | 200 to 240 ft |
| Type 3 | > 29 to 46 | 175 to 200 ft |
| Type 4 | > 46 to 70 | 145 to 175 ft |
| Type 5 | > 70 to 100 | 105 to 145 ft |
| Type 6 | > 100 to 130 | 80 to 105 ft |
| Type 7 | > 130 and Up | Under 80 ft |
Lighting distribution applied in Outdoor Luminaires
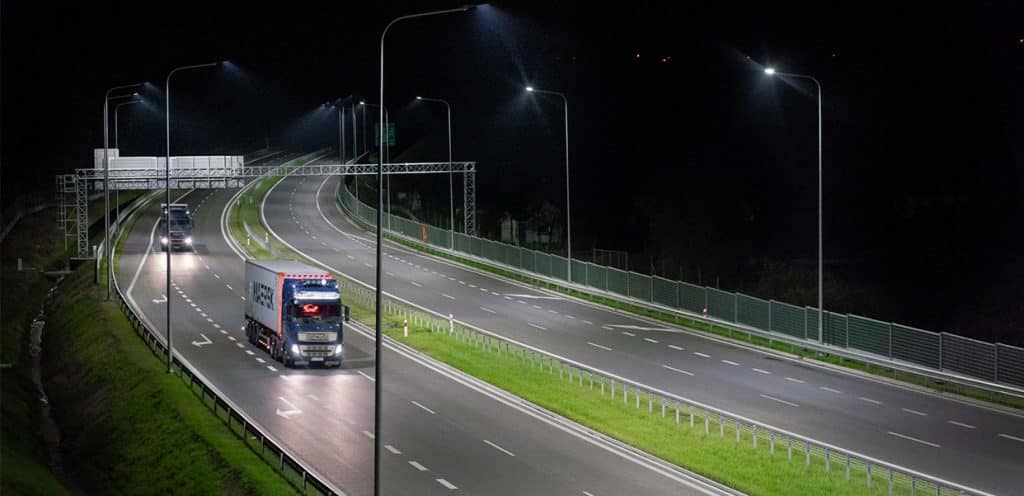
Street and Roadway
Roadway light fixtures are designed to produce fairly uniform illumination across streets and roads. They are usually mounted on arms on poles. Nowadays, LED street lights are gradually replacing HID and sodium lamps for street and road lighting. In addition to the advantages of LED itself, the development of LED light distribution makes LED street lights more reasonably evenly distribute light on the road. Usually a wide vertical light distribution allows for larger pole spacing, and a wide Lateral light distribution is suitable for wider road lighting, but may be more prone to discomfort and disability glare due to the high-angle luminous intensity. For this reason, the luminous intensity distribution can have a maximum limit at angles above 75° from the nadir. These are mentioned in IESNA Type.
Post top lighting
LED post top lights are generally used in parks, country roads, hotel roads, pedestrian areas, residential roads and parking lot lights. They are normally mounted on top of the post and creating an illuminated area in the adjacent area. This is the reason it calls post top light. Due to the particularity of its lighting place, it not only meets the lighting requirements, but also takes into account the aesthetics. Of course, its light distribution is also important, usually Type I, Type V, and Type 1MS are often used, because the roads here are generally narrow, so the narrow lateral lighting distribution is more suitable for lighting in this area. Again, Type V is suitable for this kind of place, because we only need to illuminate the area under the light fixture, similar to parking lot lighting.
Parking Lot
Parking lot lighting is a term that describes outdoor lighting, usually mounted on poles, in parking lots, paths and driveways. This type of exterior lighting is often used to illuminate areas used by vehicles and pedestrians. Parking lot lighting distribution is usually with Type III, IV, and V. These luminaires are pole mounted and can be configured in single, double or quad sets. Symmetrical and asymmetrical intensity distributions ( What’s symmetric and asymmetric lighting distribution? ) and mounting configurations provide the necessary flexibility for pole placement in the car park. For example, the lamps at the center of the parking lot can use the parking lot lights with Type V light distribution. The lamps near the edge of the parking lot can use Type III and IV lamps.
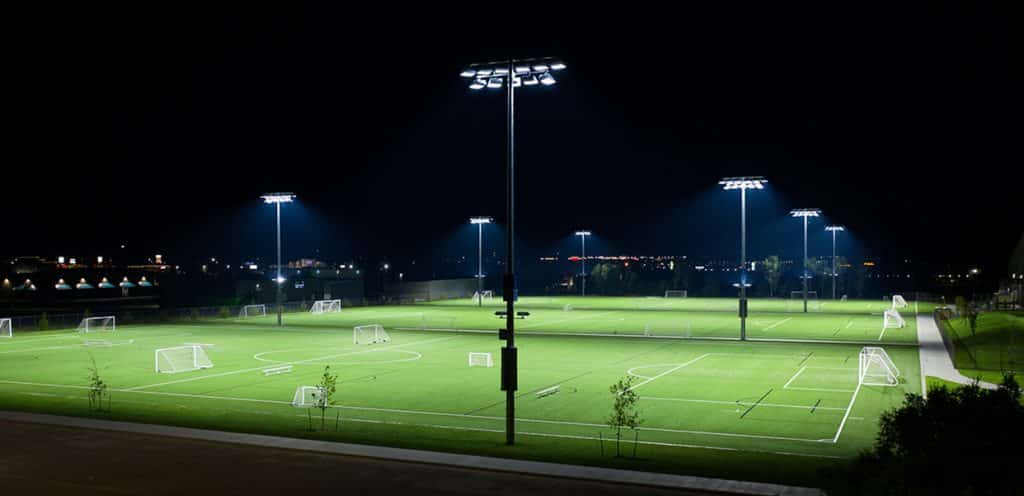
Sports Lighting
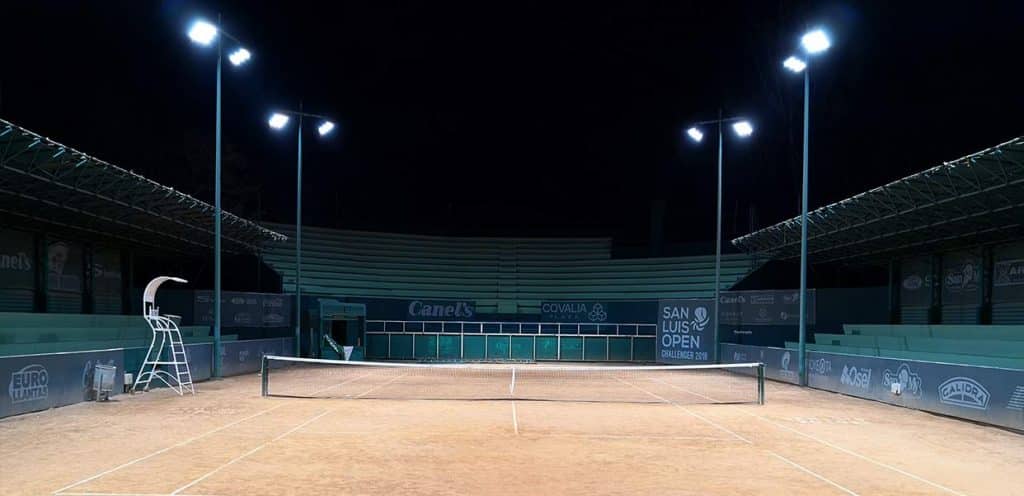
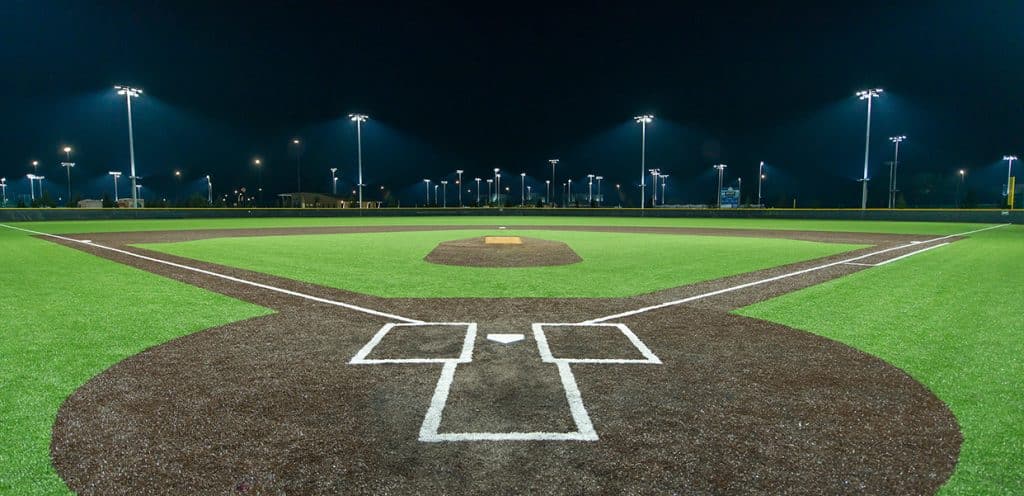
The luminous intensity distribution of sports lighting fixtures is generally very narrow, usually installed on the edge side of the court, and it is much higher than the sports area. Like football field lighting, tennis court lighting, baseball field lighting, etc. Its light distribution as well as floodlights which will be talked later are all mentioned in NEMA’s light distribution system. Some of the lamps for stadium lighting have a medium distribution, and some require a narrow distribution. The use of narrow intensity distribution luminaires almost always requires careful design to ensure correct beam overlap and proper horizontal and vertical illumination. Since aiming is a critical part of their application, these luminaires are often equipped with special aiming and locking devices.
Flood lighting
These luminaires are often used in architectural lighting and other specialty applications. These applications require luminous intensity distributions ranging from very narrow to very broad, depending on the angular size of the illuminated object and the desired effect. The light intensity distribution can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. The luminaires used for building exterior lighting can be narrow or wide, depending on the part of the building that is illuminated and its distance from where the luminaires are installed. Column lighting, accent lighting and distant mounting locations require narrow distribution. Large area lighting close to the installation site requires a very wide distribution. The lighting of billboards and parking areas sometimes requires a wide asymmetric spectrum to achieve good lighting effects.
Summary
Through this article we hope you have gained some understanding of the light distribution of different luminaires by IESNA and NEMA. This article discusses the basis of classification, how to confirm the light distribution of lamps, and the application of different light distributions in different lamps. By confirming the light distribution, you can quickly know what kind of area this IES is more suitable for lighting or what kind of road conditions. Or if you have a specific area that needs lighting, you can quickly filter from multiple light distributions to the right light distribution for the project. If you are interested in street lights, stadium lights, flood lights and post top lights with different light distribution, you can also contact us, we will recommend the best lights for you to illuminate your roads, parking lots, courts, parks or other outdoor areas more reasonably.
Related Products
Related Blogs
Related Cases
People also ask
Author introduction

Hello Customers,
My name is Taylor Gong, I’m the product manager of ZGSM Tech. I have been in the LED lights industry for more than 13 years. Good at lighting design, street light system configuration, and bidding technology support. Feel free to contact us. I’m happy to provide you with the best service and products.
Email: [email protected] | WhatsApp: +8615068758483





























